How to Select Plants that Attract Pollinators for Your Home Garden

The Importance of Pollinators in Your Garden
Creating a garden that encourages pollinators offers more than just aesthetic pleasure; it directly contributes to the health of our ecosystems. Pollinators such as bees, butterflies, and hummingbirds are essential for the pollination of many crops and wild plants, making their role crucial for biodiversity. In fact, according to the U.S. Department of Agriculture, approximately one-third of the food consumed in the United States depends on pollination, showcasing the necessity to foster environments that support these busy creatures.
When planning your pollinator-friendly garden, the selection of plants plays a pivotal role. Start with native plants, which have evolved alongside local pollinator species. Plants like coneflowers, black-eyed Susans, and milkweed not only thrive in your garden but also provide familiar food sources for local pollinators. For instance, milkweed is crucial for monarch butterflies, serving as their only host plant where they lay eggs and find nourishment.
In addition to native species, consider the blooming season of your plants. By choosing a variety of flora that flower at different times throughout the year, you ensure that pollinators have access to nutrition throughout their active months. For example, early-blooming crocuses and snowdrops can provide crucial early spring food, while late-blooming goldenrods and asters can sustain them into the fall.
The color and fragrance of your plants can also impact their ability to attract pollinators. Bright, colorful flowers like zinnias, dahlias, and bee balm not only draw the eye but are also visually appealing to pollinators. Sweetly scented plants such as hyssop and lavender can entice not just bees but also butterflies and other beneficial insects to visit your garden.
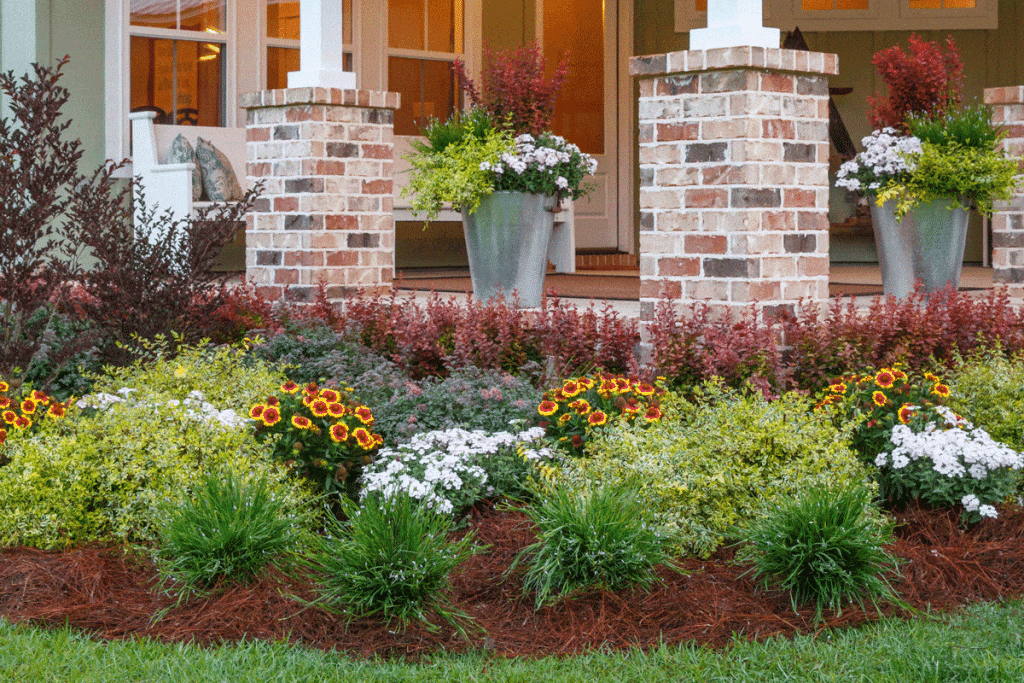
Diverse Plant Selection
A diverse plant palette can foster a richer pollinator habitat. Consider incorporating a mix of wildflowers, which are generally low-maintenance and can easily adapt to various conditions. Native wildflowers like the purple passionflower or the perennial sunflower create a vibrant tapestry of color and food for pollinators without requiring excessive care.
Moreover, herbs such as thyme, oregano, and rosemary are not only valuable for cooking but also attract a variety of beneficial insects. Flowering herbs can bring a delightful fragrance and provide food for both humans and pollinators alike. By ensuring your herb garden includes flowering varieties, you can serve dual purposes—sustaining pollinator health and enhancing your culinary creations.
Flowering shrubs like elderberry and serviceberry offer more than just food; they provide essential shelter for wildlife. These shrubs can create nesting sites for birds and act as a protective habitat for various pollinator species, helping to foster a comprehensive ecosystem in your backyard.
By consciously selecting plants and considering their impact on local wildlife, you not only create a visually appealing garden but also contribute to ecological well-being. As you nurture your garden into a pollinator haven, remember, every flower planted is a step towards encouraging a sustainable and diverse environment that benefits both nature and humanity.
DISCOVER MORE: Click here to grow your gardening knowledge
Choosing the Right Plants for Pollinators
When it comes to creating a habitat rich with pollinators, understanding how to select the right plants is vital. Not all plants are created equal; some are far more enticing to pollinators than others. To make informed choices, consider factors such as plant variety, environmental conditions, and plant placement within your garden.
Consider Plant Variety
Your plant selection should include a broad array of species that appeal to different types of pollinators. Firstly, think about a mix of annuals and perennials. Annual plants like marigolds and cosmos typically bloom for the entire season, providing a stable food source, while perennials like daisies and bee balm return year after year, offering pollinators a reliable habitat. This approach ensures you have plants blooming at various heights, colors, and forms throughout the growing season.
To help you decide, here’s a list of some excellent plants grouped by pollinator type:
- Bees: Lavender, sunflowers, and clover.
- Butterflies: Milkweed, zinnias, and lantana.
- Hummingbirds: Trumpet vine, salvia, and columbine.
When selecting plants, also consider their blooming times. Choosing plants that bloom in different seasons enables pollinators to find sustenance from early spring through late fall. For instance, you might begin with early bloomers like crocus and end with late bloomers like goldenrods.
Assess Environmental Conditions
Your garden’s specific microclimate plays a significant role in determining which plants will thrive. Take stock of the sun and shade patterns, soil type, and moisture levels. For example, if your garden is predominantly sunny, consider heat-loving plants like black-eyed Susans or coreopsis. Conversely, for shadier spots, try planting bleeding hearts or ferns, which can still provide valuable nectar and pollen.
Remember also to consider plant height and growth form. Taller plants can provide shelter for ground-nesting bees, while lower plants can serve as attractive ground cover. By layering plants of different heights, you create a sanctuary that not only looks appealing but offers accessible resources for pollinators.
Strategic Plant Placement
Once you’ve chosen your plants, strategic placement can greatly enhance their effectiveness in attracting pollinators. Group similar plants together in clusters rather than spacing them out. This creates a visual landing pad for pollinators, making it easier for them to navigate and find food. An additional benefit is that many plants will attract similar pollinators, creating a more concentrated and lively community.
Incorporating native plants into your garden design is another effective strategy. Native plants are not only hardier and easier to care for, but they also attract native pollinators due to their co-evolution. By making thoughtful selections in your garden, you won’t just be attracting pollinators, but also fostering an ecosystem that supports them.
By carefully choosing plants based on variety, environmental compatibility, and placement, you can develop a flourishing home garden that becomes a haven for pollinators. This emphasizes the important relationship between plant life and pollinators, ultimately contributing to a healthier ecosystem. As you embark on selecting plants for your pollinator garden, remember that each choice can make a significant impact!
Incorporating plants that attract pollinators into your home garden is not only beneficial for your landscape, but it also significantly contributes to local ecosystems. To maximize the effect of your garden, consider a diverse range of plants that bloom throughout the growing season. This ensures that pollinators have a consistent food source, which can lead to healthier populations of bees, butterflies, and other important species. Here are some specific plant categories that you can explore:
| Plant Type | Characteristics |
|---|---|
| Natives | Adapted to local conditions, low maintenance, and best for local pollinators. |
| Annuals | Provide continuous blooms, bringing variety and color to your garden. |
| Perennials | Lasting plants that attract pollinators year after year, promoting habitat stability. |
In addition to plant selection, it’s essential to think about the design of your garden. Grouping plants of the same species together can create a vibrant display that easily attracts pollinators. The arrangement, height, and spacing of these plants can also impact the visual appeal and functionality of your garden in attracting these beneficial insects. Research shows that increased biodiversity in garden settings can lead to higher pollinator visitation rates. Thus, a varied yet harmonious garden layout not only enhances aesthetics but also supports healthy pollinator activity.
Furthermore, consider the importance of providing shelter and nesting sites for pollinators. Incorporating elements such as native grasses, flowering shrubs, or small water features can create a welcoming environment that encourages pollinators to thrive. Remember, a well-planned garden is a sanctuary for biodiversity and an oasis for your local ecosystem, contributing positively to the environment.
DISCOVER: Click here to learn more about resilient plants for summer
Creating a Pollinator-Friendly Environment
In addition to selecting the right plants, you can boost your garden’s appeal to pollinators by fostering an environment that meets their needs. This involves considering factors like pesticide use, water sources, and habitat diversity.
Avoiding Pesticides
One of the most critical steps in attracting pollinators is to minimize or completely avoid the use of pesticides. Chemicals used in traditional gardening can be harmful or even fatal to beneficial insects. Instead, consider employing organic gardening practices that promote healthy ecosystems. Techniques such as integrated pest management (IPM) can help control pests naturally, using methods like introducing beneficial insects, such as ladybugs, or employing companion planting. By creating a chemical-free zone, your pollinator friends will feel safer to visit your garden.
Providing Water Sources
Just like any other living creatures, pollinators require water. Incorporating a water source into your garden can be as simple as a shallow birdbath or a dish filled with pebbles and water. Be sure to change the water regularly to keep it fresh and free of mosquitoes. Additionally, creating small puddles or damp soil areas can also serve as hydration spots for thirsty bees and butterflies, making your garden even more inviting.
Enhancing Habitat Diversity
Encouraging a diverse range of plants and features in your garden can significantly enhance its attractiveness to pollinators. This involves not only having various flowering plants but also incorporating elements such as shrubs, trees, and native grasses. Plants that provide shelter, such as hedgerows or butterfly bushes, can help create a structured environment that offers resting spots and nesting materials. Moreover, fallen leaves, brush piles, and natural detritus can serve as excellent habitats for ground-nesting bees and other beneficial insect species.
Choosing Color and Scent
Have you noticed that some flowers seem to attract more pollinators than others? The answer often lies in their color and scent. Brightly colored flowers, particularly in shades of yellow, blue, and purple, tend to catch the eye of pollinators from a distance. Additionally, strong fragrances are often more attractive, especially for moths and bees. Plant varieties such as goldenrods and phlox pack a fragrant punch, luring pollinators with their sweet scents. By strategically choosing colorful and aromatic plants, you can enhance the visual and olfactory allure of your garden.
Timing of Planting and Blooming
The timing of your planting can also affect the availability of resources for pollinators. Consider planning successive plantings to create a constant supply of blooms. By staggering when you plant different species, you can ensure that your garden has blooming flowers throughout as much of the growing season as possible. A well-timed garden with continuous blooms can keep pollinators coming back repeatedly, providing them with the sustenance they need.
In conclusion, creating a pollinator-friendly garden goes beyond just selecting the right plants. By employing techniques to eliminate pesticide use, providing water sources, enhancing diversity, considering flower colors and scents, and timing your plantings wisely, you will lay the foundation for a thriving habitat that attracts a multitude of pollinators. Taking these additional steps will not only contribute to your garden’s beauty but also support the vital role these creatures play in our ecosystem.
DISCOVER MORE: Click here to learn about choosing the right plants for your climate
Final Thoughts on Creating a Pollinator Paradise
As you embark on the journey of building a vibrant home garden that attracts pollinators, remember that the key lies in a holistic approach. It’s more than just about selecting plants that appeal to these essential creatures; it’s about cultivating a sanctuary where they can thrive. By embracing environmentally friendly practices, you can minimize the negative impacts of chemical pesticides while encouraging a healthy ecosystem that supports diverse wildlife.
Incorporating adequate water sources and ensuring a multitude of habitats will transform your garden into a true haven for bees, butterflies, and other vital pollinators. The importance of color and scent cannot be overlooked—flowers that bloom in vibrant shades and exude delightful fragrances will undoubtedly catch the attention of pollinators, enhancing both your garden’s aesthetic and ecological value.
Finally, consider the timing of your plantings to ensure a steady supply of nectar and pollen throughout the seasons. By fostering growth in a staggered manner, you can support pollinators year-round, reinforcing their critical role in our ecosystem while enjoying the beauty of your flourishing garden.
By investing time and energy into creating a pollinator-friendly environment, you contribute not only to the health of your local ecosystem but also to the broader global movement aiming to protect our planet’s biodiversity. Delve deeper into the specifics of each plant type and understand better what your local pollinators need. This knowledge will empower you to make informed choices, ensuring that your garden becomes a beacon of life and color, teeming with activity and beauty.


